Menstrual cycle influences the spread of mutant cells in mammary tissue
Leuven/Amsterdam/Cambridge, 5 September– A team of researchers at the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology, the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Oncode Institute and the University of Cambridge have discovered that a defensive mechanism connected to the menstrual cycle plays a role in spreading mutant cells within mammary tissue. A new study published in Nature describes how the growth and subsequent removal of extra milk ducts in breast tissue during the menstrual cycle can contribute to the spread of mutant cells leading to large mutant fields prone to develop tumors.
Although tissue in healthy individuals may look completely normal, it can contain large fields of mutant cells that are capable of growing into a tumor. The more cells within a normal looking, but mutant field, the higher the chance that one of these cells will behave abnormally and develop into cancer. To date, researchers are unsure of how these large fields of mutant cells develop in normal tissue.
Some theories propose that mutant cells spreading over large fields of tissue may play a crucial role in the initiation and recurrence of human breast cancer. An international team of researchers led by Professors Colinda Scheele at the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology, Jacco van Rheenen at the Netherlands Cancer Institute and Oncode Institute, from Cancer Grand Challenges team PRECISION, funded by Cancer Research UK and KWF Dutch Cancer Society, and Benjamin Simons at the University of Cambridge has now published new findings suggesting that a mechanism responsible for normal remodeling of breast tissue during the menstrual cycle is a potential driver of breast cancer development.
When remodeling does not go to plan
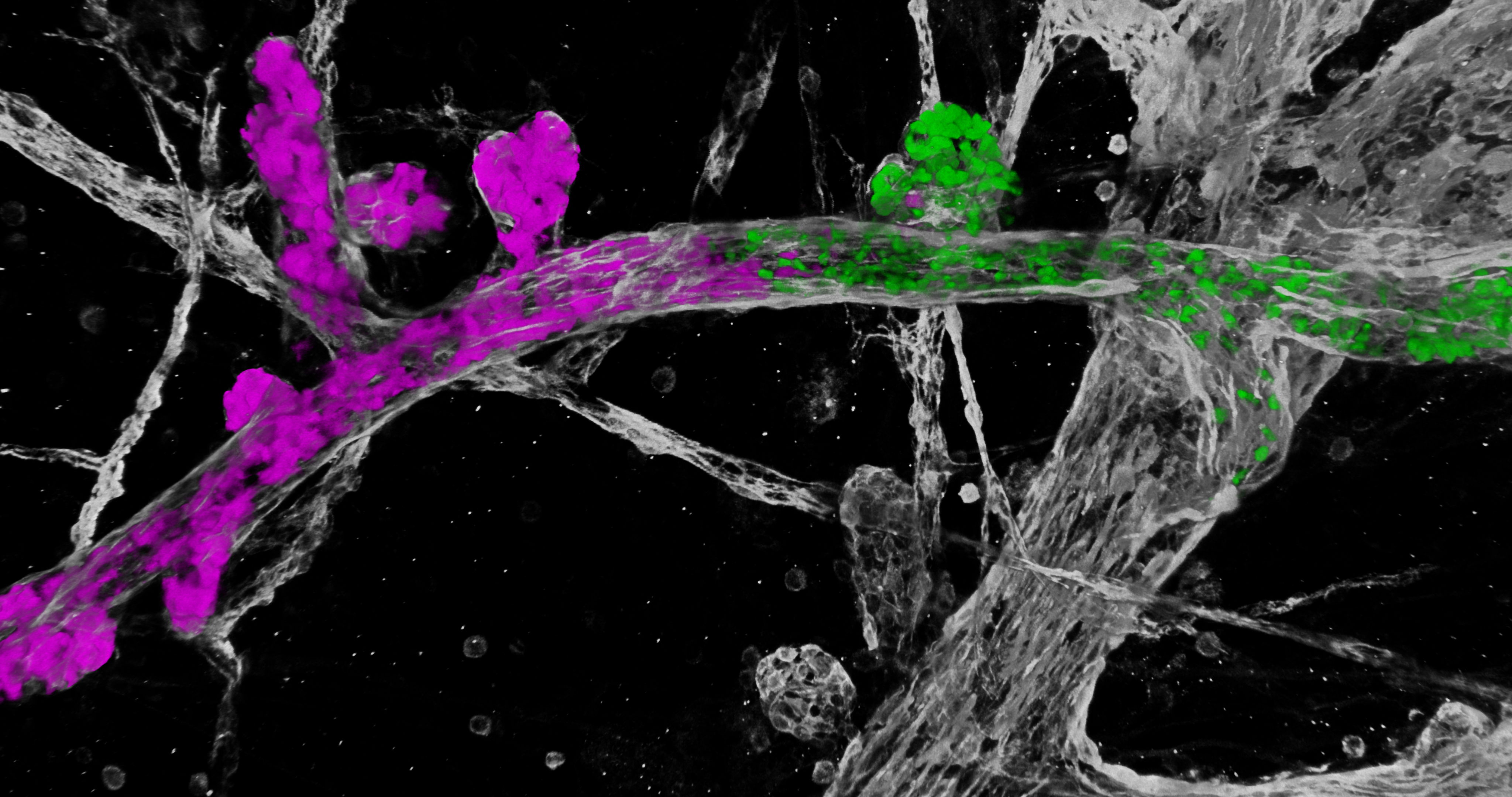
During the equivalent of the menstrual cycle in mice, the mammary glands go on a remodeling spree. Heightened estrogen levels ensure the creation of small alveoli that grow into milk-producing units upon pregnancy. However, when there is no pregnancy, the body recognizes that these alveoli serve no purpose. At the end of the cycle, the body therefore breaks down these milk ducts removing most of the expanded cells.
Even though this mechanism seems to be very effective at cleaning out excess cells, including mutant cells, it appears it is not infallible. The body cleans up most of these cells at the end of the cycle but some mutant cells, by chance, may survive this process. Instead, the tissue remodeling now allows these cells to proliferate and spread within the normal tissue. Thus, the natural tissue remodeling in the breast appears to be a double-edged sword: on the one hand it leads to the natural removal of excess (both normal and mutant) cells, on the other hand it facilitates the expansion of a few mutant cells within the healthy tissue.
Colinda Scheele: “In our study, we observed the evolution of mutant cells before they developed into cancer. More specifically, we labelled both healthy and mutated stem cells in the mammary tissue of mice and tracked their behavior over several months. Our findings showed that the menstrual cycle influenced the behavior of the labelled cells and allowed some of them to spread over large distances. "

Jacco Van Rheenen: “Our findings demonstrate that with each menstrual cycle, there is a slight chance that mutated clones can become larger and spread over large areas within the breast tissue. This also means that a higher number of cycles increases the chances of this happening and therefore the chances of developing cancer in time. It also potentially explains why pregnancies and breast feeding decreases breast cancer chance."
While this study provides a better understanding of the earlier stages of tumor formation, more research is needed to determine how and where healthcare practitioners can intervene to ensure cells carrying mutations do not develop into cancer. As a next step, the team hopes to examine human tissue from donors to verify if the same mechanisms are at work in the human body.
The research described in this scientific paper was made possible thanks to the Cancer Grand Challenges PRECISION team and through the financial support of the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation, the FEBS excellence award, the Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek, EMBO, and the European Research Council.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07882-3
Joran Lauwers
Questions from patients
A breakthrough in research is not the same as a breakthrough in medicine. The realizations of VIB researchers can form the basis of new therapies, but the development path still takes years. This can raise a lot of questions. That is why we ask you to please refer questions in your report or article to the email address that VIB makes available for this purpose: patienteninfo@vib.be. Everyone can submit questions concerning this and other medically-oriented research directly to VIB via this address.
About the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology
Cancer has many causes. Often it is a combination of lifestyle, environmental factors and genetic variation. We need to fight cancer on many fronts, and this can only be done by using knowledge. The VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology researchers unravel new mechanisms in order to develop both specific diagnostic methods and treatments.
About the Netherlands Cancer Institute
The Netherlands Cancer Institute, founded in 1913, is among the top 10 comprehensive cancer centers, combining world-class fundamental, translational, and clinical research with dedicated patient care. We have set ourselves a bold goal: a cure for every cancer, and excellent care for every patient. We aim to do this through innovations. We innovate by combining the best scientific research and treatment for people with cancer.
Learn more at https://nki.nl
About Oncode Institute
Oncode Institute is an independent research institute dedicated to realizing breakthroughs in the understanding of cancer and translating them into clinical practice for the benefit of cancer patients. The institute is founded on three pillars: Excellent Science, Collaboration, and Valorization – together creating impact. The institute unites over 800 researchers at 13 partnered research institutes, all dedicated to achieving the same mission: to accelerate breakthrough discoveries and speed up their translation into new diagnostics and treatments for cancer patients.
Learn more at www.oncodeinstitute.nl
About Cancer Grand Challenges
Co-founded in 2020 by two of the largest funders of cancer research in the world: Cancer Research UK and the National Cancer Institute, Cancer Grand Challenges supports a global community of interdisciplinary, world-class research teams to come together, think differently and take on some of cancer’s toughest challenges. These are the obstacles that continue to impede progress, and no one scientist, institution, or country will be able to solve them alone. With awards of up to £20m, Cancer Grand Challenges teams are empowered to rise above the traditional boundaries of geography and discipline to make the progress against cancer we urgently need.
Every two years, Cancer Grand Challenges invites the global research community and patient advocates to share their views on the greatest obstacles standing in the way of making vital progress against cancer. The Cancer Grand Challenges Scientific Committee, comprising some of the world's most eminent researchers, then meets to discuss and debate the ideas submitted and recommends to Cancer Research UK a set of complex challenges, that it believes can be solved. Cancer Research UK and the National Cancer Institute make the final decision on which challenges should be posed to the research community.
International teams are then invited to apply for up to $25 million in funding to support innovative, interdisciplinary research to solve them, with the successful teams announced the following year.





